Google'scrawlers patrol the Internet and sequentially store (index) web page information in a database.
To check the detailed Index status, use the search console, but we will also explain how to check the index of URL of other sites to which you do not have authorization.
- Using the Google search command site:
- Using the Search Console
2. How to check Index status in the Search Console
- Site-wide (directory-by-directory) Index status
- Page-by-page index status
3. Points to consider when checking index status
- Error
- Enabled (with warning)
- Enabled
- Excluded
- How to check Index status of a specific page
4. How to respond if a website or page is not indexed
5. Summary
1. How to check Index status
There are two ways to check the indexation rate.
Using the Google search command site:
You can find out the approximate number of indexed pages by entering the site: plus URL into Google search.
Unlike the search console method described below, this method has the advantage that it can be used even for sites without search console privileges. Still, it is not accurate and should be taken only as a reference value.
Entering a domain or directory after site will display the number of indexed hits.
And look at the image above.
There are 55 results, but the displayed results are about 20 posts (2 pages).
So it does not matter if the number of posts displayed in the google search results is less than the number of your posts.
For commands other than site:, check the following.
Using the Search Console
Use the Search Console to investigate the exact Index status.
If you have not yet registered your site, please do so in advance.
Use the Index Coverage Report if you want to check Index status of the entire site or under a directory.
On the other hand, if you want to check Index status of each URL, use the URL inspection tool.
If the site is not indexed, you can also submit an index request directly.
The following sections will explain the key points of using Search Console to check index.
2. How to check Index status in the Search Console
You can check Index status of URL within a property by using the Index Coverage Report in the Search Console.
If you want to know Index status of each directory, create a URL prefix property in advance.
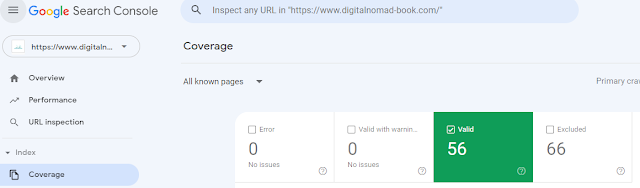
You can check the Index Coverage Report from the menu "Coverage" in the Search Console.
The following four types of statuses are displayed in the coverage report. You can check Index status as well as troubleshooting.
Error
You can see the number of pages that have failed to crawl or submitted to the sitemap but have not been indexed.
Clicking on a detected message at the bottom of the screen displays a detailed screen where you can check the target URL.
It is recommended to take action from here first.
Valid with warning
It is a page registered in the index but has a warning. Generally, there are only a small number of these pages, and they have little impact on the site, so you may want to put them off.
Valid
It is a page that has been indexed. Pages that are "submitted and registered" are not a problem.
Especially for large sites, you may want to check "Indexed, but not submitted to sitemap."
If URLs listed should be indexed, such URL should be sent from the sitemap. If duplicate pages listed should not be indexed, they should be removed from the index for crawling and optimization purposes with noindex, 404, etc.
If duplicate pages listed should not be indexed, they should be excluded from the index for crawling and index optimization purposes.
Excluded
These pages have not been submitted to the index due to factors other than the errors mentioned above.
There is little need for action if the number of pages in this category is small compared to the number of "active" pages. If the number of "Excluded" pages is large, it may harm crawler migration, so it is recommended that measures be taken in advance.
In particular, URL that falls under duplicate, soft 404, crawled (detected) - unregistered, etc., should be checked with priority.
How to check Index status of a URL Inspection page
Using the Search Console's URL inspection tool, you can also check Index status of specific pages (whether they are indexed or not, date of last crawl, canonical URL, etc.).
URL inspection is performed by entering the target URL in the search box at the top of the console screen and pressing the Enter key.
- Registration index status (registered, registered but with problems, not registered)
- Coverage report (date and time of the last crawl, whether it was successfully crawled, whether Googlebot crawled it for smartphones (whether it has already migrated to mobile-first index), canonical URL indexed)
- Enhancements (Mobile usability, Breadcrynbs) with or without errors
3. Points to consider when checking index status
First of all, it is essential in SEO whether a page is indexed or not because if a page is not indexed, it will not appear in search results.
While there are trillions of pages on the Web, Google's resources are finite, so Google does not index every page.
Google will try to index more (and faster) sites (pages) worth displaying in search results and will not index or delay those that are not.
It is best to think of index in terms of two axes: site-wide (directory-based) and page-by-page.
Site-wide (directory-by-directory) Index status
We check whether the number of pages indexed corresponds to the increase or decrease in the number of pages in the site or directory.
If the number of pages is increasing, but the index number is decreasing, or if the index number itself is decreasing, there is a possibility that some anomaly is occurring, such as Google not being able to access the pages.
Be especially careful if the index number is decreasing rapidly.
Page-by-page index status
In particular, it is good to know how long it takes for newly published pages to be indexed.
If there is a certain amount of pages that are not indexed, it is also recommended to investigate the index rate by checking whether individual pages are indexed.
4. How to respond if a website or page is not indexed
To be indexed by Google, crawlers must find URL that should be crawled. There are three ways to get found.
- Internal/external links
- XML sitemap
- Index request function of URL inspection tools
If a page is not indexed, we will prepare internal links and ensure that the URL is submitted from a sitemap.
If the page is still not indexed or is challenging to index, use the URL inspection tool's index request function.
It is difficult for pages on sites that are not updated frequently or are not of high quality to be indexed immediately.
If you want to increase the speed of being indexed, you can keep adding quality content regularly.
5. Summary
From an SEO perspective, a page that Google does not index cannot be found in a search, no matter how meaningful the content is, and is as good as not existing.
Not being indexed can be due to technical factors such as crawl errors or software factors such as content quality, so we recommend that you manage your website while regularly checking Index status.
To learn more about SEO, check out the post below.